About
Couples can significantly increase their chances of conception by having intercourse on or before the day of ovulation. One way to improve the timing is to use an ovulation calculator.
An ovulation calculator estimates the day a woman will ovulate based on the first day of her last menstrual period (LMP). The calculator works by adding cycle length to LMP and then deducting the luteal phase, which is usually defaulted at 14 days, to arrive at a predicted ovulation date.
Our ovulation calculator uses your last menstrual period to predict the date you are likely to ovulate and the days you are likely fertile.
Important Note: Treat all results from any ovulation calculator as being estimates only. It is recommended that all results are confirmed by extra testing. We hope you enjoy our calculator!
When Am I Most Fertile?
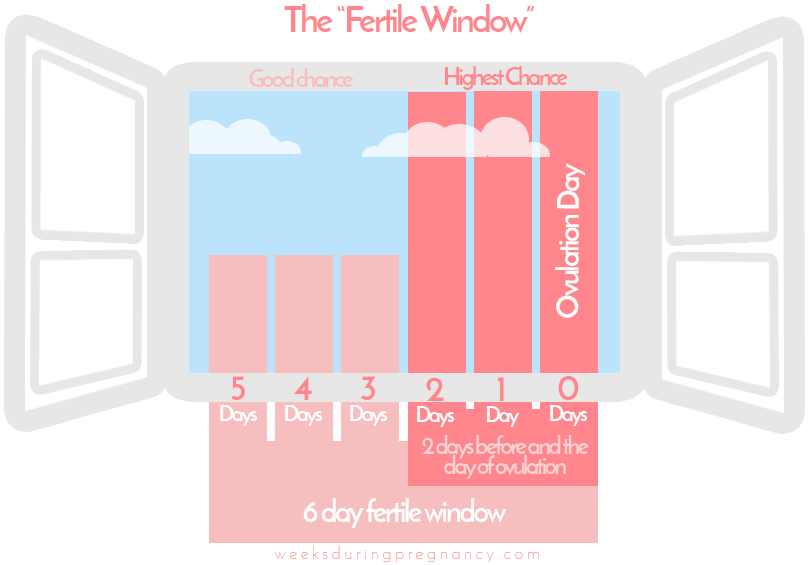
The fertile window: Research shows that most pregnancies are the result of intercourse in the 5 days leading up to ovulation or on the day of ovulation.[2] This period of time is often called the Fertile Window.
The fertile window starts 5 days before ovulation and ends on the day of ovulation.
Fertility is especially high 2 days before ovulation and on the day of ovulation.[2]
The calculator will show your predicted ovulation date and fertile days.
Trying to Conceive
Couples trying to conceive (TTC), should have intercourse during the woman's fertile window and especially during the 2 days before ovulation and/or on the day of ovulation.
It can also be helpful to focus on days your vaginal mucus is watery and stretchy, like raw egg white.[3]
Alternative Method for Timing Intercourse
Knowing your ovulation and fertile dates is helpful but not crucial. If you regularly have intercourse 2 or 3 times a week, probability indicates you will hit the fertile window[2] whether or not you know the details of your cycle.
Not Trying to Conceive
If you do NOT want to become pregnant, remember that almost any day is potentially a fertile day depending on your cycle length and timing of ovulation.[1]
Why you are Fertile Before you Ovulate
When you have intercourse, the sperm released by your partner can survive for several days. If you ovulate in the following hours or days after intercourse, sperm and egg can meet and conception can occur. A sperm remains able to fertilize an egg for approximately five days after being released during intercourse.[2]
How Ovulation Calculators Work
Ovulation calculators work by adding the menstrual cycle length to the date the last menstrual period started and then deducting the luteal phase to arrive at a predicted ovulation date.
(LMP + Cycle length) - Luteal Phase = Ovulation
LMP = First Day of Last Menstrual Period
Cycle Length = Length Between First Days of Cycle
(LMP + Cycle length) - 14 days = Ovulation
LMP = First Day of Last Menstrual Period
Cycle Length = Length Between First Days of Cycle
Why the Ovulation Calculator Deducts the Luteal Phase:
If a woman's menstrual cycle is shorter or longer than average, the follicular phase - from the onset of menstruation until ovulation - is probably the reason since the follicular phase is known to be quite variable. The luteal phase - from ovulation until the next period begins - is generally more consistent in length, at an average of 14 days.
Since the luteal phase is reasonably constant in length, it is traditional to assume that it is 14 days long and that ovulation therefore takes place 14 days before bleeding starts.
Example: Calculating Ovulation
To calculate your ovulation date yourself, use the same formula that the ovulation calculator uses:
(LMP + Cycle length) - Luteal Phase = Ovulation
LMP = First Day of Last Menstrual Period
Cycle Length = Length Between First Days of Cycle
Last menstrual period started = Jan 1, 2017
Average cycle length = 30 days
Calculation:
Ovulation = (Jan 1 + 30 days) - 14 days
Ovulation = Jan 31 - 14 days
Ovulation = Jan 17
Predicted ovulation date for the January cycle = January 17, 2017
Predicted next menstrual period = January 31, 2017
Ovulation Calculators can only Estimate Dates
Most ovulation calculators are based on the assumption that ovulation occurs 14 days before menstrual bleeding begins, however some research suggests that as few as 10% of women actually ovulate 14 days before menstruation.[1] Even women with regular 28 day cycles do not necessarily ovulate 14 days before their periods begin.[1]
Despite the variable nature of ovulation, an ovulation calculator provides a platform or base to start from if you are seeking to optimize your chances of pregnancy. Ovulation calculator results should be confirmed by using an ovulation test kit or monitor, see here.
How to Calculate Your Average Menstrual/Ovulation Cycle Length
Your cycle length is the number of days from the first day of one menstrual period through the day before the first day of the next period.
If you have a record of your previous cycles, count how long each cycle was over the last x amount of months. Add them all together and then divide the total by x to find the average.
If your last 6 cycles lasted 28, 32, 26, 32, 31, and 30 days.
Add 28+32+26+32+31+30 = 179
Divide 179 by 6 = 29.8 days
Round the result up or down
Your average cycle length for the last 6 months is 30 days
How to Calculate Your Fertile Window Yourself
[(LMP + Cycle Length) - Luteal Phase] - 5 Days = First Day of Fertile Window
Cycle Length = Length Between First Days of Cycle
Luteal Phase = Defaulted to 14 Days
Last menstrual period = January 1
Average cycle length (see above) = 30 days
Anticipated next menstrual period = January 31
Expected ovulation date for January cycle = January 17
Fertile window = January 12 to January 17
Most fertile = January 14 to 17
Possibly fertile = January 10 and 11
If you already know your ovulation date, subtract 5 days from your ovulation date (find the day which is 5 days before your ovulation date). The date you obtain is the start of your fertile window and the day of ovulation is the final day of the window. You may also be fertile 2 days before this.[1]
How to Calculate Your Luteal Phase
As discussed above, the luteal phase is now known to be quite variable, even in women with consistent 28 day cycles. But it is still reasonable to begin with the assumption that your luteal phase starts 14 days before menstruation, as long as you bear in mind that this may not be the case for you.
If you don't know your ovulation date: Assume your luteal phase is 14 days (default assumption) but know this may not actually be so for you.
If you do know your ovulation date: The luteal phase is the number of days from ovulation to the day before your next menstrual period.
How to Calculate your Follicular Phase
If you don't know your ovulation date: Begin with the first day of your last period (LMP) and add your average cycle length. Then deduct 14 days (average length of the luteal phase). The remaining days are the estimated days of your follicular phase.
If you do know your ovulation date: The follicular phase is the number of days from the first day of your period to the day you ovulate.
How to Know More Accurately When you are Ovulating
We suggest you use the ovulation calculator to find your expected ovulation date and fertile window and then use any of the following methods to help confirm your ovulation date. A combination of more than one indicator is more reliable than any one on its own.
Methods of Detecting Ovulation: Signs of Ovulation
- Mucus: Vaginal
mucus changes during the menstrual cycle as hormone levels rise and fall.
Before ovulation, mucus is thin and clear, slippery, and stretchy (ideal for
intercourse and for sperm to travel). After ovulation, it either reduces or
thickens; either way, it changes.
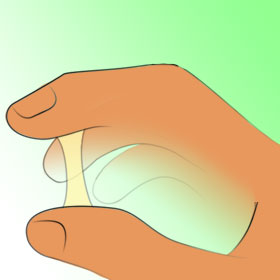
Not fertile, mucus is dry and not stretchy - Not fertile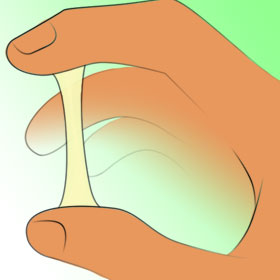
Semi clear, can be creamy. Should be stretchy - Semi fertile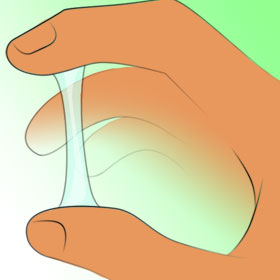
Clear and stretchy - Highly fertile. - Ovulation Predictor Kits: Ovulation
predictor kits test urine, saliva, or sweat and predict approaching
ovulation. Depending on the type of kit used, ovulation can be predicted by
as much as four days ahead.
- Twinges: You
may feel a small twinge, or feelings of cramp in the lower abdomen at the
time you ovulate. Such signs are only noticed by one in five women but you
may be one of the five.
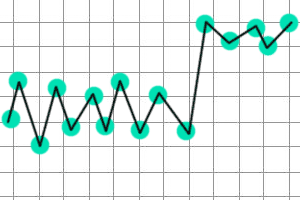
- Basal Body Temperature (BBT): Once
ovulation has occurred, your basal body temperature rises. A few days before
you expect to ovulate, start taking your basal body temperature in the
mornings, following the specific instructions supplied with your basal
thermometer. Continue until you notice a higher reading (about half a
degree) which indicates you have ovulated. Make sure to have intercourse in
the days leading up to your expected ovulation date since the likelihood of
conception is slim once ovulation is registered by the BBT thermometer.
Taking BBT readings can help you chart your ovarian cycle; if you miss your
fertile window this month, it can help you plan for next month.
Dates Provided by this Calculator are Only Guidelines
References
- 1.Wilcox, Allen, Dunson, D, and Baird, D "The timing of the "fertile window" in the menstrual cycle: Day specific estimates from a prospective study." BMJ 321 (2000): 1259 - 1262.
- 2. Wilcox, A, C. Weinberg, and D. Baird, A. "Timing of sexual intercourse in relation to ovulation: Effects on the probability of conception, survival of the pregnancy, and sex of the baby." The New England Journal of Medicine 333 (1995): 1517 - 1521. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199512073332301
- 3. Bigelow, J. et al., "Mucus observations in the fertile window: A better predictor of conception than timing of intercourse." Human Reproduction 19 (2004): 889 - 892. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deh173
- 4.Gougeon, A. "The early stages of follicular growth." In Biology and pathology of the oocyte: Role in fertility, medicine and nuclear programing, edited by A Trounson, R. Gosden, and U. Eichenlaub-Ritter, 50-61. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013.
- 5.Baerwald, A. et al. "Ovarian antral folliculogenesis during the human menstrual cycle: A review." Human Reproduction Update 18 (2012): 73 - 91. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmr039